Heart Attack
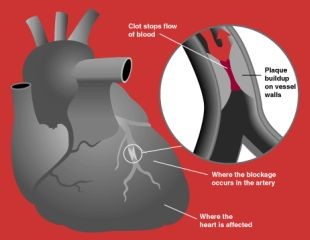
This occurs when one or more of the arteries supplying the heart become totally occluded and a part of the heart muscle is permanently starved of blood. Heart attack is also medically known as a MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION.
This is sometimes the end result of atherosclerosis and will probably follow repeated and more painful angina attacks. It also can occur when a fatty deposit (atheroma) of the artery wall becomes dislodged and travels down the arteries until it blocks a smaller vessel. This is referred to as an EMBOLISM. It can also be caused by a blood clot (THROMBOSIS): a blood clot may form as the blood’s platelets become activated as they rub across the rough artery wall caused by atheroma. The platelets become ‘sticky’ and can form a clot which blocks an artery at a certain point.
Depending of the location of the occlusion and therefore the amount of tissue death (necrosis), will depend on the severity of the heart attack. There may be mild, moderate or severe disability and in some cases sudden death.
Depending on the severity and location of the artery blockage, it may cause severe rhythm disturbance and the heart will stop beating. This is known as CARDIAC ARREST.
SYMPTOMS of a HEART ATTACK: The symptoms of a heart attack may be similar or more severe than that of angina, but generally lasts longer. The pain is sometimes described as a ‘tightness, pressure or heaviness in the chest’. The pain of a heart attack may last anywhere from 30 minutes to several hours and will not respond to cessation of stress/activity like angina, nor to mild pain killers, warmth or change of position. In addition, the following may also be experienced:
- perspiration
- feeling cold and clammy
- breathlessness
- nausea and vomiting
- pain radiating to the jaw and/or down the left arm
If you suspect you are suffering from a heart attack, you should dial 999 and get immediate medical attention.
It is also possible to suffer from a SILENT HEART ATTACK – this is where no symptoms are experienced, but this may leave evidence.